
BIGCCS - International CCS Research Centre
CO2 value chain
Contact person
CO2 chain analysis, environmental impacts, and safety
Overall objective:
To enable CCS value chain assessment as a means for selecting the most cost-effective options for CCS and to evaluate additional parameters such as environmental impacts and risk assessment.
Contribution to one or more of the overall goals/objectives of BIGCCS
- The CCS value chain integrates assessment of the whole chain (capture, transport and storage) in order to select the most cost-effective CCS chain and decrease the overall cost of implementing CCS chains.
- The CCS value chain methodology also includes other assessments such as the environmental impact in order to evaluate CCS chains completely and avoid problem shifting.
Achievements thus far:
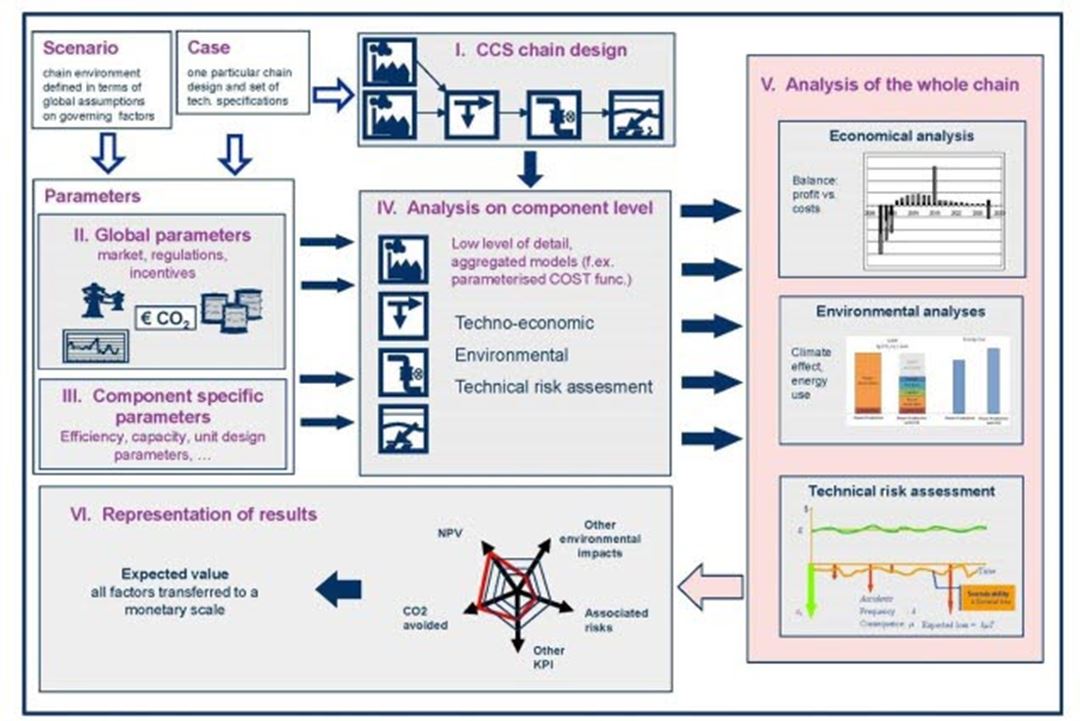
- Development of a consistent and transparent multi-criteria framework for assessment of CCS chains (Figure 1).
- Development of modules estimating the costs and climate impact of different parts of the CCS chain (capture, transport and storage).
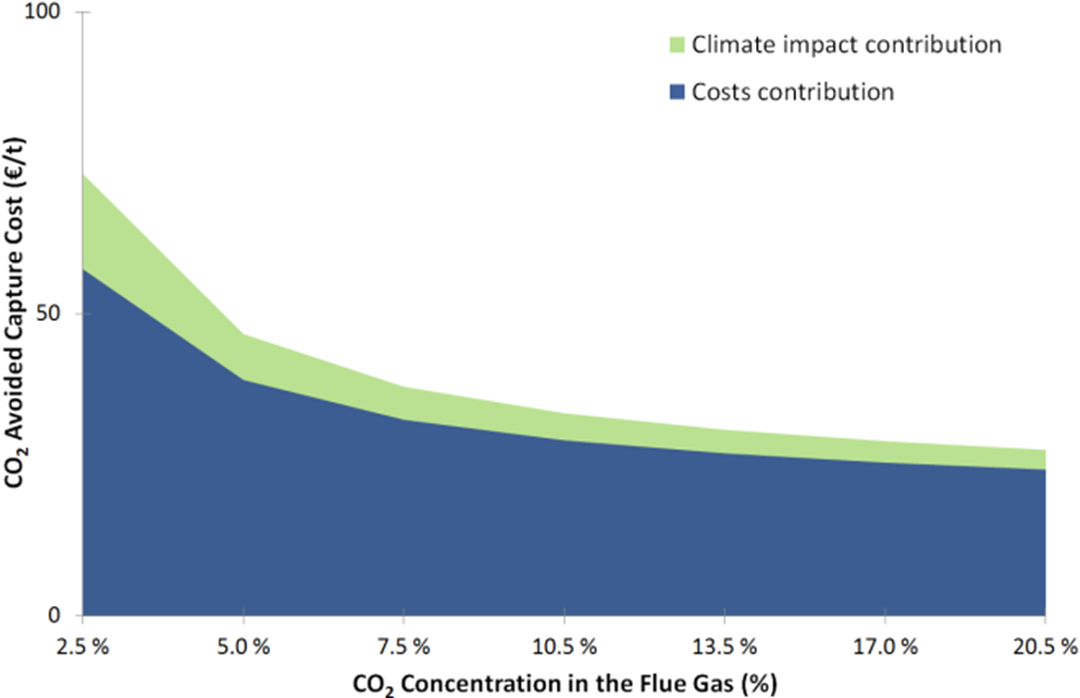
- Assessment of the impact of the CO2 concentration on an amine-based post-combustion CO2 capture process by including the technical, economic, and environmental assessments together as shown in Figure 2.
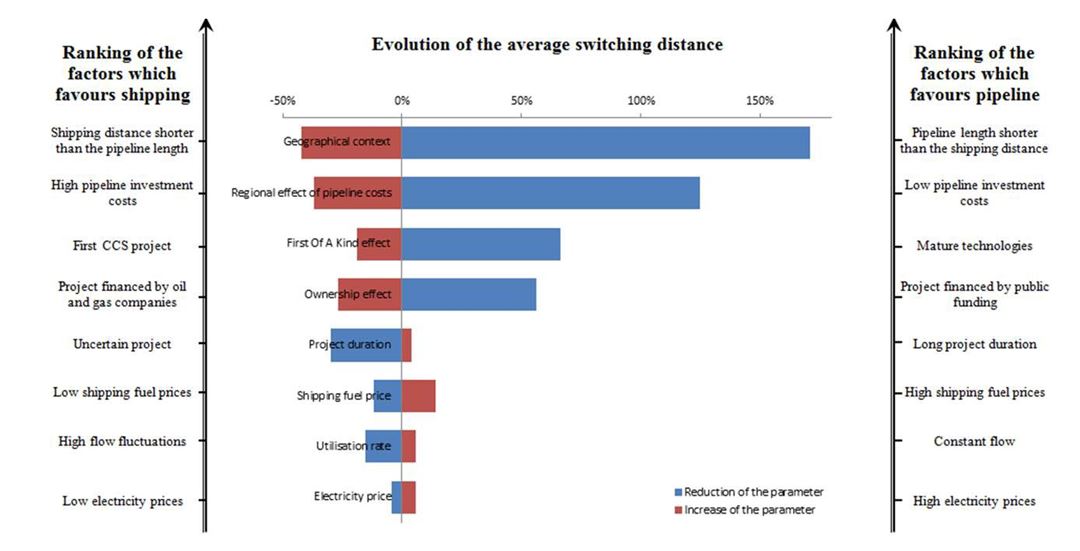
- Systematic evaluations of pipeline and shipping transportation and quantifications of how important parameters impact this decision (Figure 3).
- Quantifications of the impact of the CO2 capture plant capacity on the capture cost in the case of a coal power plant with flexible profile to promote better capacity selection and better investment decisions.
- Economic evaluations of flexibility and associated plant operation parameters through an analysis of a base load coal fired power plant with flexible post combustion CO2 capture in a market with cyclical electricity price patterns.
- Number of papers, presentations, etc.
Related publications
- A standardized Approach to Multi-criteria Assessment of CCS Chains
- Carbon chain analysis on a coal IGCC — CCS system with flexible multi-products
- Benchmarking of CO2 transport technologies: Part I—Onshore pipeline and shipping between two onshore areas
- Multi-criteria Analysis of Two CO2 Transport Technologies
- Comprehensive assessment of CCS chains – Consistent and transparent methodology
Collaboration with other FMEs on Economic and Policy Incentives for CCS (new task in 2014)
Overall objective:
To explore measures and policies that stimulate innovation and dissemination of CCS through collaborations with other FMEs on social science and policy.
Contribution to one or more of the overall goals/objectives of BIGCCS
This task examines policy tools and measures that stimulate further development of CCS chains to reduce the cost per ton of CO2, and required market-based incentive mechanisms for CCS chains to become commercial.
Goals 2014:
- Develop collaborations with the other FMEs including politics and social science perspectives established in 2010
- Especially with the CICEP (Strategic Challenges in International Climate and Energy Policy) led by Professor Arild Underdal, University of Oslo.
- Conduct workshops with these FMEs to exchange knowledge, information and results that could lead to case studies on economic and policy incentives for CCS.
Related publications
- A standardized Approach to Multi-criteria Assessment of CCS Chains
- Carbon chain analysis on a coal IGCC — CCS system with flexible multi-products
- Benchmarking of CO2 transport technologies: Part I—Onshore pipeline and shipping between two onshore areas
- Multi-criteria Analysis of Two CO2 Transport Technologies
- Comprehensive assessment of CCS chains – Consistent and transparent methodology
