Ensuring an adequate food supply for the escalating human population is a great challenge. Crop losses and value degradation caused by plant diseases are major constraints to food security globally. Fungicides are important tools in management of plant diseases caused by fungal and oomycete pathogens. However, reliance on fungicides is not sustainable in the long run due to development of fungicide resistance, concerns regarding health effects and costs associated with pesticide removal from water resources. Integration and use of new, non-chemical strategies are therefore crucial for continued production of high-quality food in a sustainable manner.
The END-IT project focuses on systems and strategies for management of fungal diseases with non-chemical options. The project partners are BIOVIT-NMBU (project leader, plant genetic research, optical treatment of fungal diseases), SINTEF (fungal spore detection system), Wageningen University (screening and selection), NIBIO (socio-economic analysis), Bama Gruppen AS (end-user) and Gartnerhallen (end-user).
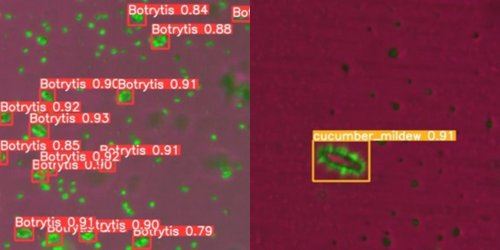
SINTEF's main contribution to END-IT is development of a technical solution for online detection and quantification of pathogen inoculum presence in the plant surroundings. The innovation includes development of a low-cost field microscope that can sample and image fungal spores which have diameters as small as 5 micrometres, and development of machine vision algorithms that can classify the spores. The system was tested in four different greenhouses during summer 2023.
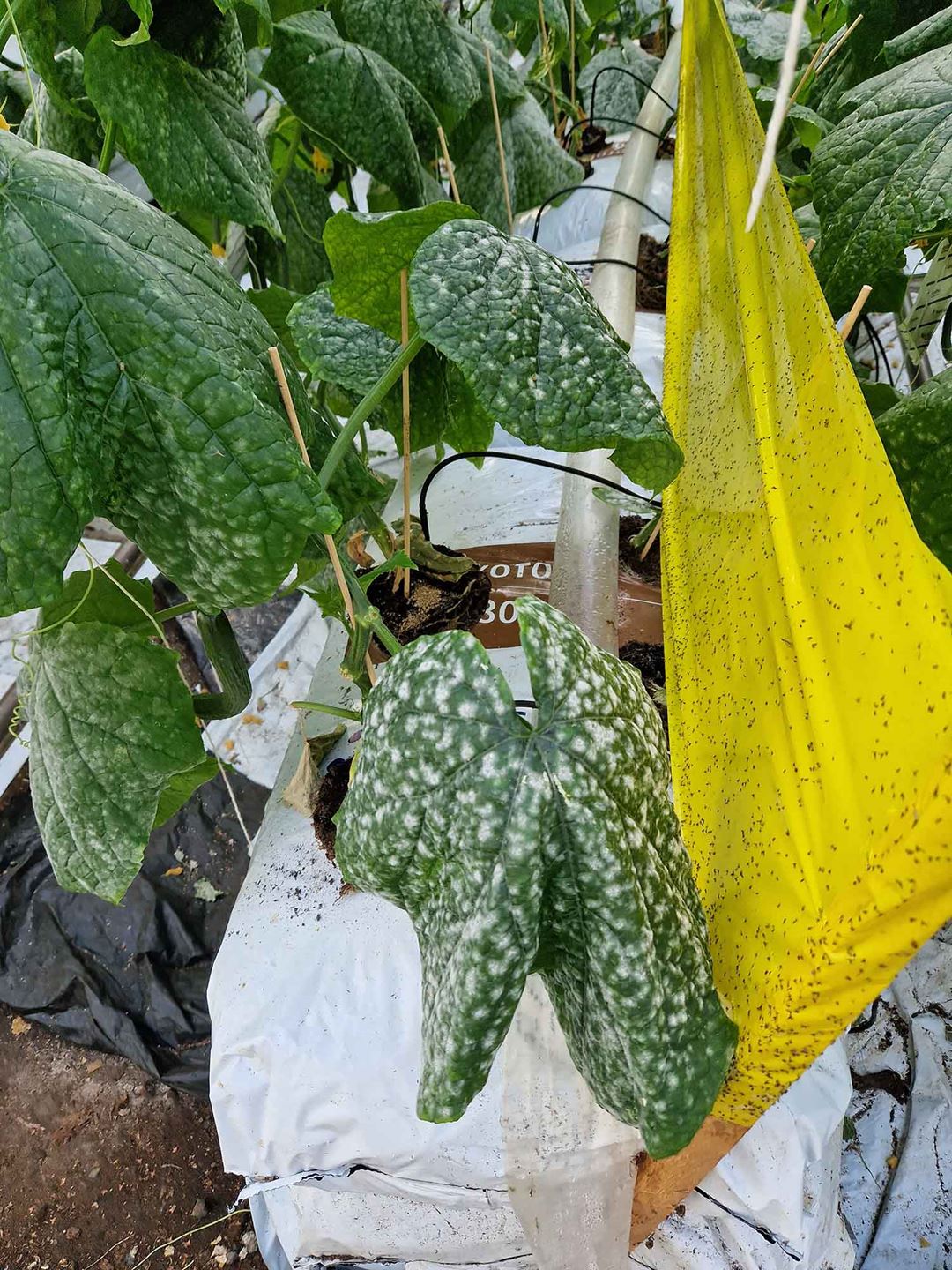


The spore detection system will be combined with NMBU's work on optical treatment of fungal diseases, and together this will constitute an optical crop treatment system that ensures sustainable and environmentally friendly crop production of high-quality produce. Improved crop yield, reduced waste, and reduced use of fungicides will increase profitability to society.