The current recycling practices for Photovoltaic (PV) modules waste are inadequate, often only recovering materials of low volume and value. To achieve both economic viability and sustainability, the recycling process must be refined to efficiently reclaim all constituent materials from PV waste in a quality high enough for incorporation into new PV modules, while minimizing environmental impact.
The APOLLO project seeks to revolutionize this process by adopting a circular economy approach, bridging the gap between legacy recycling efforts, future PV production, and subsequent recycling cycles.
Through these efforts, APOLLO is contributing significantly to the development of sustainable and efficient recycling methodologies, laying the groundwork for a more sustainable future in critical material usage and recovery.
A key innovation of APOLLO is the establishment of a pilot line with the capacity to process significant amounts of PV waste. This initiative is expected to reclaim sufficient materials to produce sufficient remanufactured silicon, alongside various prototype PV modules.
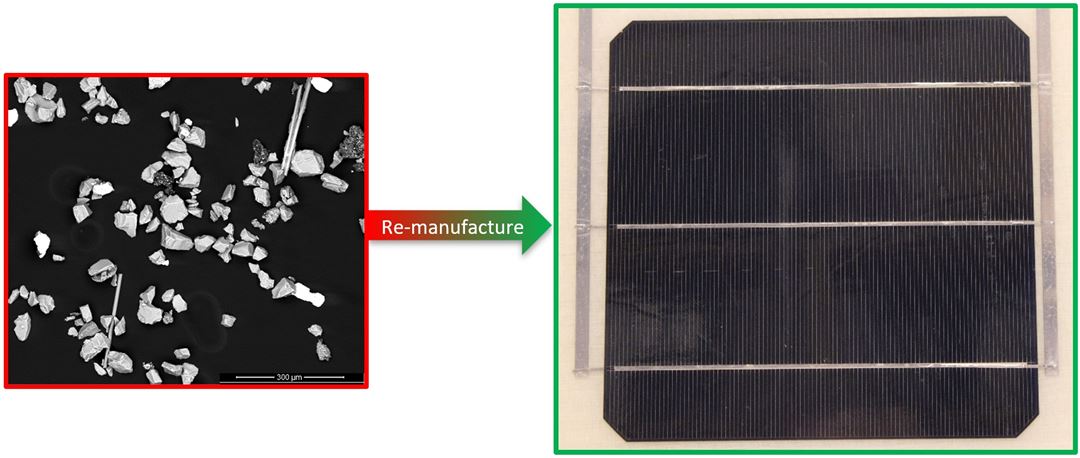
SINTEF Industry leads the work on material remanufacturing and aims innovate and test a novel gaseous refining technique at the pilot scale, specifically designed for the deep removal of boron-doped elements from recovered silicon (Si). SINTEF is also dedicated to enhancing the efficiency of recycling routes by extracting technology-critical metals, ensuring valuable resources are reclaimed and reutilized effectively.
The APOLLO consortium includes 18 partners from 9 countries, covering the whole PV value chain from material and process innovation to PV manufacturing and recycling.

