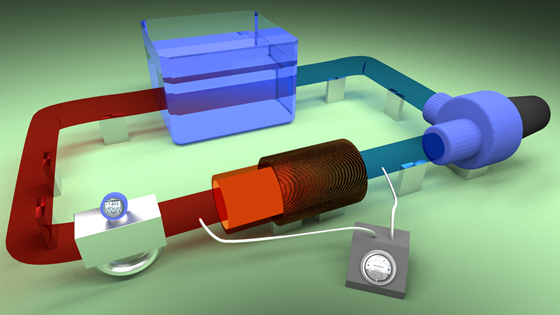
FerroCool
FerroCool is an experimental project that will investigate ferrofluid heat transfer. It is an early step towards realizing a novel, efficient and reliable cooling concept that uses magnetic nanofluids.

FerroCool is an experimental project that will investigate ferrofluid heat transfer. It is an early step towards realizing a novel, efficient and reliable cooling concept that uses magnetic nanofluids.

EMPIG, in cooperation with Kværner, will develop an always-clean cooling system (ACS). Through multidisciplinary competence at SINTEF, and a close collaboration with Kværner, that will manufacture and assemble the main parts of the ACS prototype, the...

This project would investigate how smart grid technology can be utilized in the electric distribution grid to reduce interruptions in the electricity supply and socio-economic costs of interruptions.

SINTEF possesses internationally unique laboratory facilities for multiphase flow research that have had huge benefits for the Norwegian oil industry and for the Norwegian industry cluster based on multiphase flow technology.

SINTEF and Institutt for Energiteknikk (IFE) have entered into agreement with seven companies on a new and exciting data collection project. The recently upgraded laboratories at Tiller and Kjeller now go directly into industrial use.

Demonstration of the next generation standardised integrated cooling and heating packages for commercial and public buildings based on environment-friendly carbon dioxide vapour compression cycles.

The primary objective of this project is to develop a methodology for optimized selection of energy storage solutions in hybrid ship power and propulsion systems.

The goal of the SmartPower project is to demonstrate the usefulness of modern optimisation methods for demand response applications in energy markets. To this end, we develop a prototype for optimised power matching/load balancing in large scale...

The overall aim is to create the foundations for commercializing an automotive derivative fuel cell system in the 50 to 100 kW range, for combined heat and power (CHP) applications in commercial and industrial buildings.

Managing the transition to a smart bioeconomy.

The goal of RICAS2020 is to provide an innovative design concept of an Underground Research Infrastructure to develop technologies by which the storage of very high amounts of “green” energy will be possible.

High temperature heat pumps for efficient utilisation of low temperature surplus heat

Risk reduction through climate adaptation of buildings and infrastructure

Snow conditions have an important impact on nature and human society. In Norway, one third of the annual precipitation falls as snow and snow information is important economically (hydropower), for infrastructure (construction safety and transport...

The goal of this project is to increase the understanding of the interaction between the quality of incoming materials, the hardening process and the resulting products. Thus, it is aimed to understand better how variations of incoming materials...

Metals are and will continue to be a pre-requisite for modern society; houses, cars, planes, trains, computers and mobile phones - all rely on metals. To achieve sustainability, metals need to be produced with an energy- and natural resources...

Approximately half of buildings energy demand is related to heating and cooling. District heating is an important technology in improving the energy efficiency of heating systems in cities and districts, because it enables waste heat sources to be...

This project generated new and validated functionalities in the transient multiphase simulator LedaFlow(TM) in a new area of application: flow assurance predictions for well and risers.