Knowledge of thermodynamic properties of fluids is essential in order to optimize design and operation of processing equipment used in the energy sector. Thermopack provides robust and accurate modeling of equilibrium and non-equilibrium properties of fluids, as well as mixtures of fluids, electrolytes, solids and hydrates. Advanced and accurate laboratory measurements are used to support model development. Numerical solvers are available for the most common thermodynamic operations (e.g., flashes, saturation lines, and critical points). The main applications of Thermopack has been for CCS, natural gas, refrigeration agents and hydrogen purposes.
Open source:
A limited feature open-source version of thermopack is available on github. Our intentions are to make all features of our in-house thermopack code available in in the open-source version.
Current usage of Thermopack:
- Thermodynamic model development: (a) SAFT EOS model development supported by NVT and Gibbs Ensemble Monte Carlo methods, as well as molecular dynamics (MD) simulations; (b) Implementation, testing and benchmarking of existing models
- CFD simulations: Multi-phase energy-volume flashes have been developed to enable direct calculation of thermodynamic properties during simulation (see the CO2 Dynamics software)
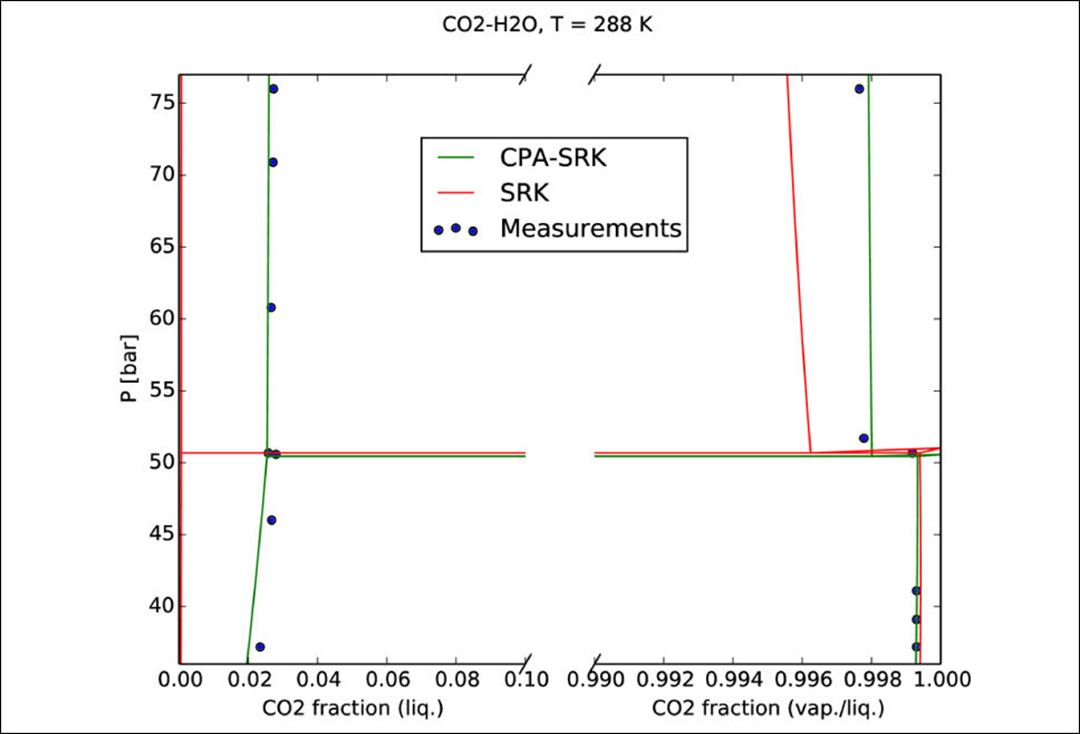
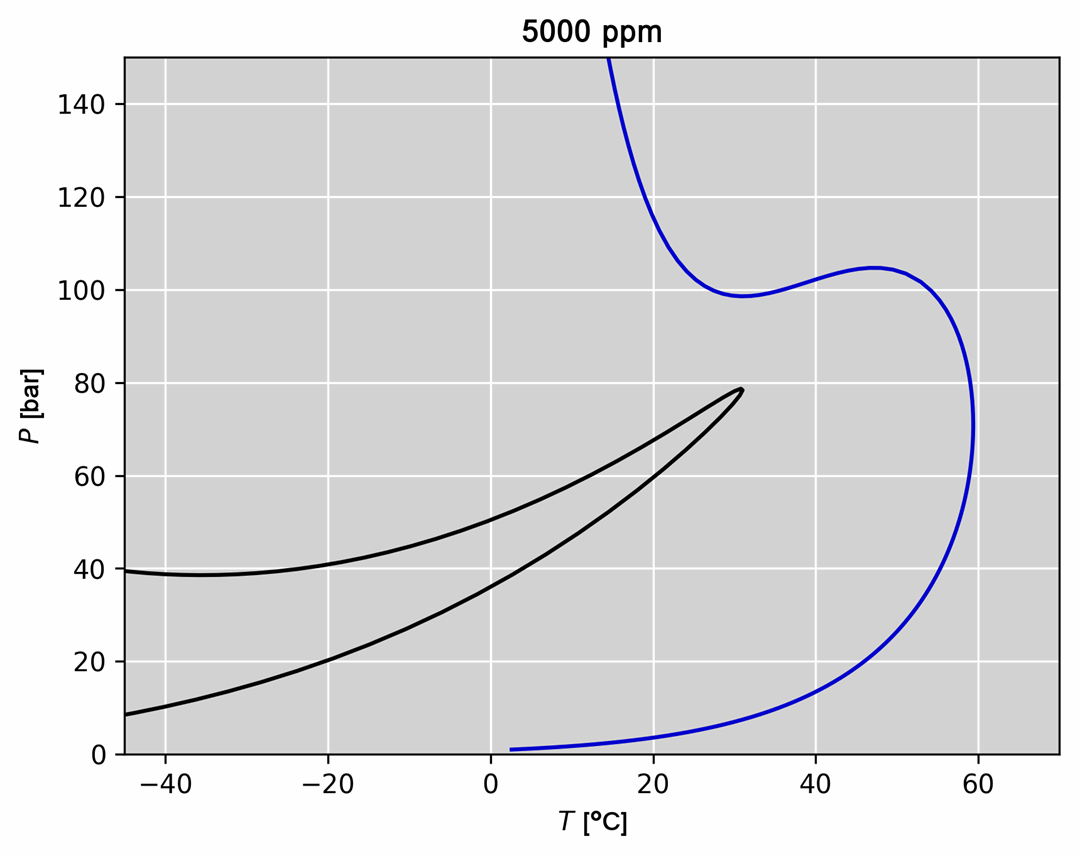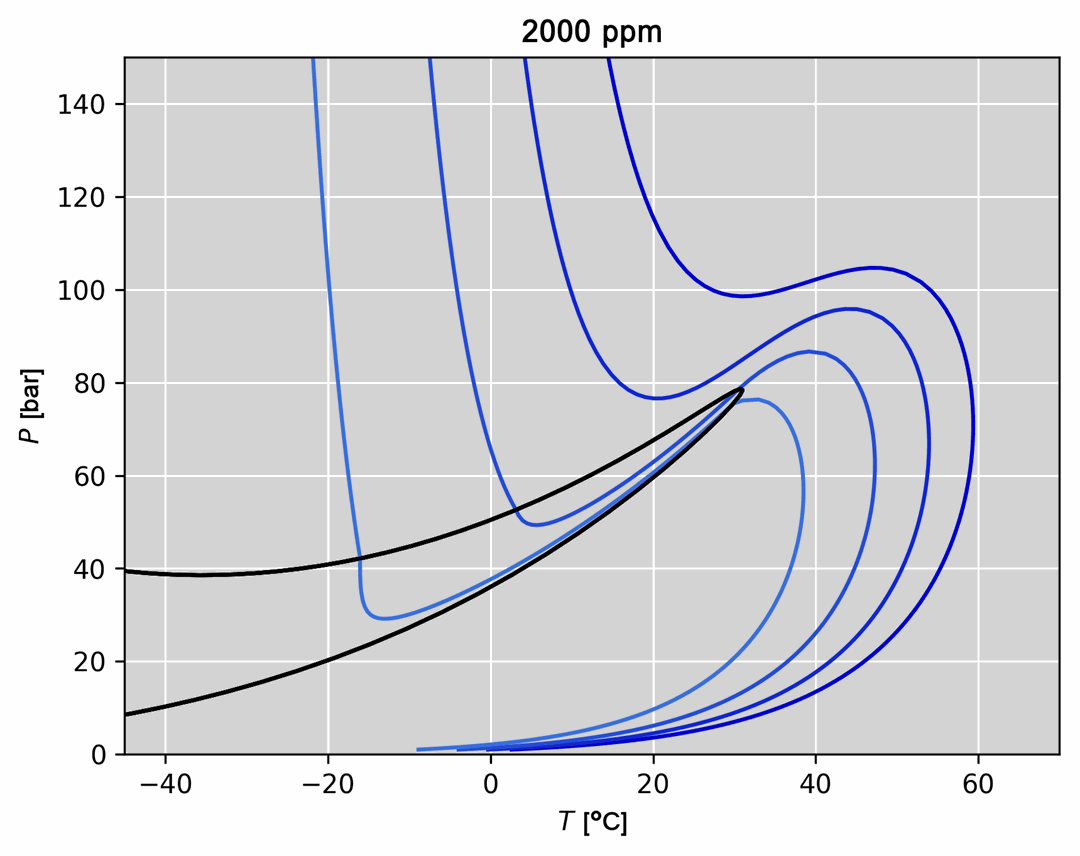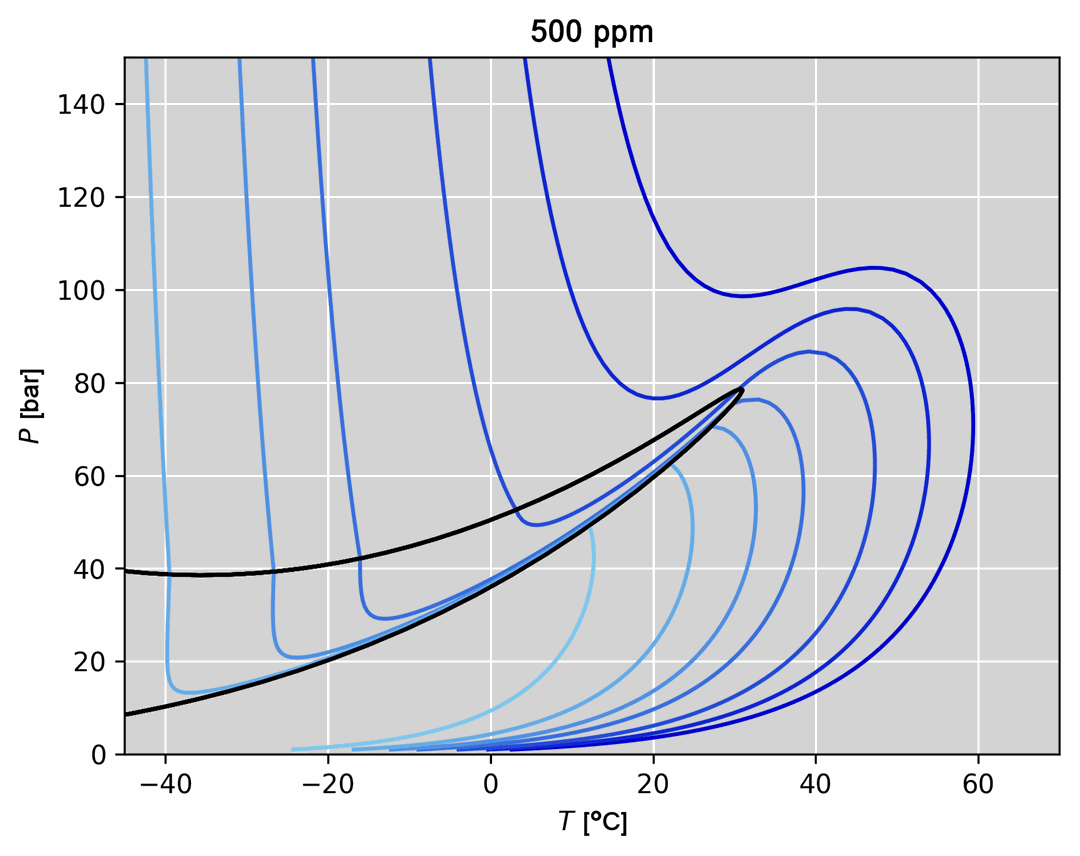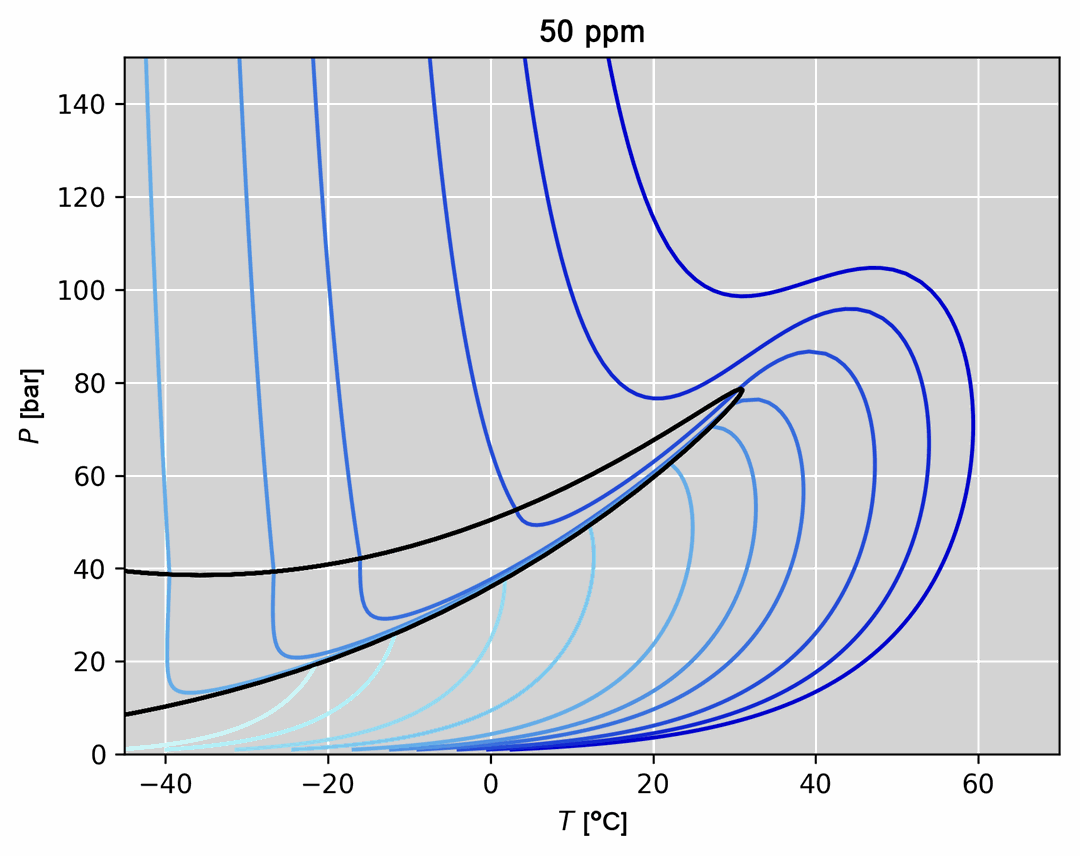
- Thermodynamic model regression and comparison to experimental data (an example is given in the figure below)
- Steady-state simulations and optimization. In particular, modelling and design optimization of complex heat exchangers
- Experimental planning
- Visualization of thermodynamic spaces and processes
For further reading:
- Thermodynamics
- #SINTEFblog: Open source code: Thermopack software perfoms thermodynamic calculations